If you were lucky to escape ransomware infection from WannaCry or Petya this year, there is one more threat to deal now. In the last couple of days or so, a new ransomware has emerged called by the name “Bad Rabbit”.
Like other Ransomware does, Bad Rabbit also encrypts all the files on the PC and asks for a hefty ransom amount for retrieval. This ransomware however not only targets individual consumers, it has been successfully infecting corporate networks with ease since it was detected.
Corporates across Russian, Ukraine, Germany, and Turkey have been hit by this ransomware. As per Avast, Poland and South Korea have also seen small outbursts of Bad Rabbit Ransomware.
Confirming the reports, The U.S. Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT) issued an alert asking individuals and organizations against paying the ransom, saying that paying ransom does not guarantee successful retrieval of infected files.
How Bad Rabbit Ransomware infects
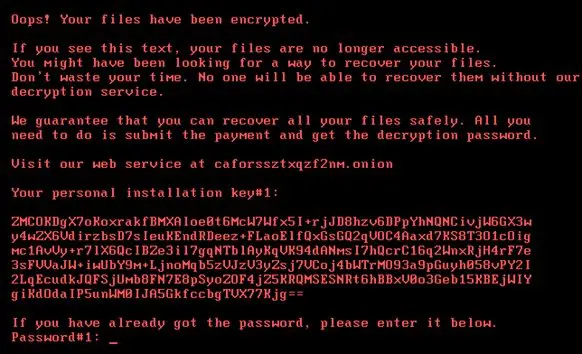
Bad Rabbit Ransomware spreads using drive-by downloads on hacked websites. It infiltrates PCs through a fake Adobe Flash installer while the victim is on a hacked website. As per the reports, the attackers till now have targeted mainly news or media websites, using them as the launch pad distributing fake installer to victims. Remember there is no flash update, but only a dropper for the malicious install.
The success of the attack is purely based on the wisdom of the victim agreeing to download malware disguised fake Adobe Flash installation.
Once Bad Rabbit Ransomware infects a PC on the network, it starts looking for any stored login credentials using the open-source tool MimiKatz. Thereafter exploiting the same credentials it tries to break away to other PCs on the network too.
After successfully breaking the defenses of PCs on the network, it goes about its job of encrypting files including those used for Windows Office, images, videos, audios, emails and archives making use of the open-source DiskCryptor utility.
What is the Ransom Amount?
Bad Rabbit Ransomware replaces victim’s PC’s Master Boot Record and reboots the machine while posting a ransom amount of 0.05 Bitcoin (about $280) to be paid to a specific Bitcoin wallet.
Encryption Scheme
As per Kaspersky, Bad Rabbit encrypts files with the following algorithms:
- AES-128-CBC
- RSA-2048
It estimates all running processes and compares the hashed name of each process with embedded hash values.
How to protect against Bad Rabbit Ransomware
Here are things you can do:
- Create files called C:\Windows\infpub.dat and C:\Windows\cscc.dat and remove all write permissions for it.
- Disable WMI service
Apart from this, observing self-caution rather than relying on traditional antivirus program is the key to avoid any ransomware. Most antivirus software nowadays fails to detect Ransomware attacks, because malware infections rarely rely on code that has already been identified as potentially dangerous. They try to fox the victim in downloading or clicking malicious links and emails.
Ensure that you are having backups of your important files. Segregating parts of your computer networks so that ransomware cannot infiltrate an entire system is another precaution that you can take.
From an organization point of view, observe strict policy on giving default permissions to employees. If anyone has the permission to download and install software then they will have the ability to install Bad Rabbit on your network. Lastly, ensure you have your network and any devices, drivers connected to it up to date.
Leave a Reply