Malvertising and malicious activities of hackers have affected a number of popular websites. And the matter of concern here is that the hackers have used doubleclick.net and Zedo for making these attacks. These popular advertising networks, one being a subsidiary of Google for online ads (doubleclick.net) and a popular advertising agency (Zedo) are not directly involved; but the hackers have exploited their ads by messing with their code. However, the good news is that Google was quick and has taken out the malicious advertising campaign. The action was taken on Friday morning.
What exactly happened due to malicious advertising campaign
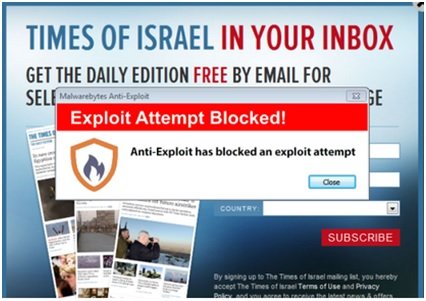
The researchers from Malwarebytes found that Malvertising had affected websites such as The Jerusalem Post, Times of Israel and even last.fm. As per this post, there is more than what meets the eye. They suspect that this is an ongoing malicious advertising campaign, that’s taking place on a larger scale and is affecting a lot of popular websites.
Malwarebytes explains how they detected malicious activities:
“The malware payload distributed onto unsuspecting visitors was identified as Zemot by Microsoft in their MSRT for September. Looking at our logs we first detected this new attack pattern on August 30th, at 2 AM. These are the URLs we caught. What is important to remember is that legitimate websites entangled in this malvertising chain are not infected. The problem comes from the ad network agency itself.”
The post further says:
“We rarely see attacks on a large scale like this, so we highly recommend that people keep their systems up-to date, with current antivirus and anti-malware protection. Malwarebytes Anti-Exploit also detects and blocks these attacks without using any sort of signatures.”
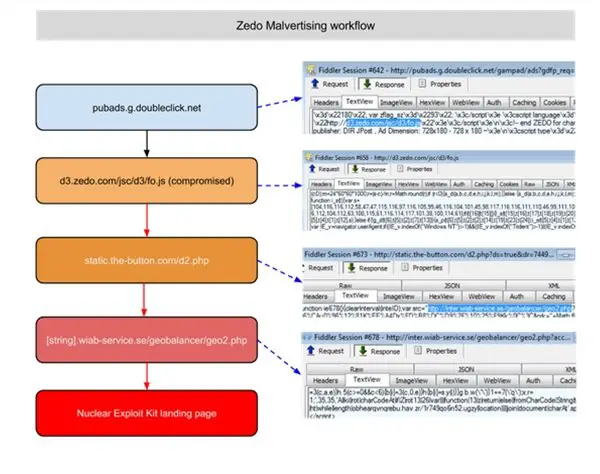
The researchers at Malwarebytes have also described the workflow of Zedo Malvertsing, which looks as follows:
We recently posted information about malvertising and how to avoid it. Malvertising is about compromising your computer, by downloading a short malicious code on to it, when you hover on or click on an advertisement. Some adverts will even download malicious code to your computer, while the website is still loading in the background. In such cases, by simply visiting a website, users can get infected via Drive-by-downloads.
Leave a Reply