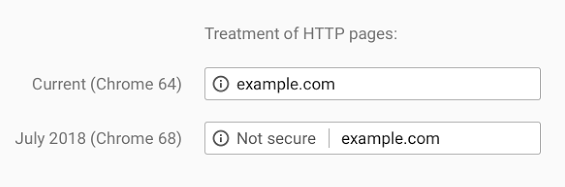
Google Chrome has been pushing the websites to migrate to the more secure HTTPS encryption as opposed to the current HTTP encryption. Starting from now the browser will mark all the websites on HTTP as “Non-secure.” Remember the padlock icon we rely on to trust the website? Well, that won’t be displayed on site that is still using HTTP encryption.
Chrome to mark HTTP pages as “Non-Secure”
As confirmed by Emily Schechter, Google security product manager, the changes will come into effect starting from Chrome 68 which is scheduled for a July rollout. Needless to say, this push is squarely aimed at getting the webmasters to migrate to HTTPS which is a relatively secure encryption standard.
This is what Emily had to say about the move,
“For the past several years, we’ve moved toward a more secure web by strongly advocating that sites adopt HTTPS encryption,” she further add that “And within the last year, we’ve also helped users understand that HTTP sites are not secure by gradually marking a larger subset of HTTP pages as ‘not secure
The implementation of HTTPS is very important as it prevents malicious attempts like the man-in-the-middle attack and enforces much stricter security. This means that any data that is being transmitted/received from the website to the server is safe, and the secure sign is an assurance that the data hasn’t been tampered with. The statistics are also pretty much skewed, according to Google, only 81 out of top 100 ranked global websites now use HTTPS.
That being said migrating to HTTPS might be a relatively easy task for a smaller site. However, it is a bit of a herculean task for older websites with a lot of content on it. To migrate the website, the webmaster first has to secure the content. On the contrary, the HTTPS will make your site more secure and will also be preferred by the Google Ranking algorithm.
Leave a Reply