There is no doubt that Ransomware and malware authors are gained advanced skills to trick users, as the technology is advancing. Recently, Microsoft Malware Protection Center has reported that cyber criminals and malware writers are using a combination of improved .lnk scripts to install Kovter and Locky ransomware on many computers. Along with the improved .lnk scripts, they are also using well-maintained download sites to transport Kovter ransomware to the users’ computers.
What is Kovter ransomware
The Kovter Ransomware carries out the commonly used Police Ransomware scam. Under this scam, the malware tricks users into believing that they have broken some law (copyrighted material or illegal pornography). A full-screen threatening message along with the local police logo appears and locks the victim’s computer. As a result, the unsuspecting users pay the ransom in order to unlock their PC. Though there are several other Police Ransomware Trojans, Kovter Ransomware is a relatively new on the block.
How Kovter ransomware is transferred to the users’ PC
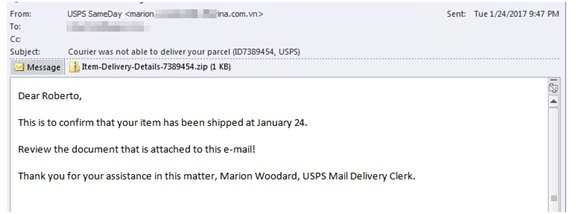
Not long ago, Microsoft Malware Protection Center has reported that an email campaign was distributing .lnk files with a malicious script. And this malicious script was the carrier of the very infamous Locky ransomware. In this process, malware authors have attached the malicious .lnk with the emails. When the users were opening these attachments, files executed a PowerShell script that performed a download routine. In fact, more recently, a more complex version of the .lnk scripts was found to be delivering more malware from more download sites.
The recently improved .lnk files have five or more different hard coded domains. When users open these files, the script attempts to download the payload malware. Earlier, it was limited to Locky ransomware; but now the script also downloads Kovter ransomware.
The team at Microsoft Malware Protection Center mentions how the script works to install Locky as well as Kovter ransomware.
“The script attempts to access a specific location in the domains by using a parameter. It does this for all domains, one by one, until it is able to successfully download its payload. If unsuccessful in the first pass, it uses another parameter and goes through the five domains again. It exits after a second pass and still no successful download. The use of multiple domains and the technique of storing the rest of the URL as a parameter is a way to circumvent URL filtering solutions. All the script needs is one URL that is not blocked in order to successfully download malware.”
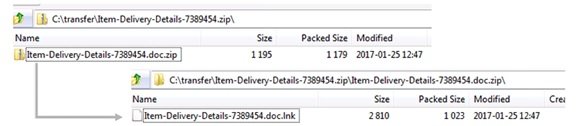
Most of the malicious attachments that come from the malware authors for infection purpose are multi-layer .zip files. Out of the two, the second .zip file consists of the .lnk file.
The Kovter ransomware like malware is a serious threat to the unsuspecting users. Only good antimalware programs and practicing caution can avoid the attacks of a ransomware.
To know more about the Kovter ransomware, read the complete blog on Microsoft Malware Protection Center.