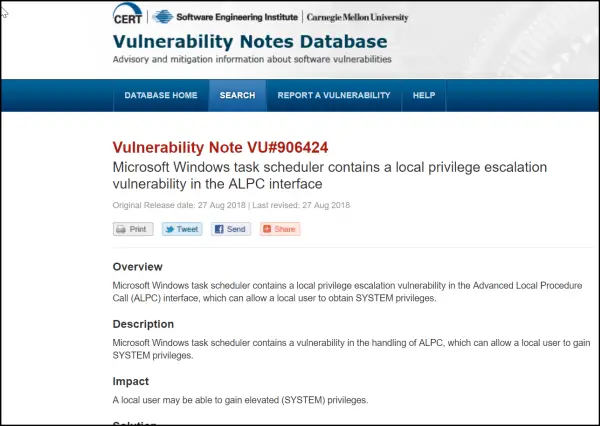
A recent finding published by CERT (Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon University) in its Vulnerability Notes Database highlights a worrying situation. The report suggests the Microsoft Windows Task Scheduler contains a vulnerability in the handling of ALPC that can allow a local user to gain SYSTEM privileges.
Windows Task Scheduler local privilege escalation vulnerability exposed
Most computer operating systems like Windows are designed for use with multiple user accounts. As such, everyone is given certain abilities as privileges. Common privileges include viewing and editing files while System privileges are protected privileges. These privileges help in prohibiting any unauthorized actions.
However, a vulnerability in the Windows Task Scheduler used by multiple Microsoft Windows products could allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain access to system privileges. The issue was publicly disclosed by SandboxEscaper in a document written by Will Dormann.
He mentioned that the Microsoft Windows task scheduler contains a vulnerability in the handling of ALPC that can allow a local user to gain System Privileges. ALPC interface is an evolution of the LPC interface introduced in Windows Vista. Its functions are smaller and reused in different parts of the interface.
As of now, the CERT/CC is currently unaware of a practical solution to this problem. Also, there’s no statement available from the vendor regarding this vulnerability.
For more information, see this page.
Leave a Reply