Windows Defender Application Control from Microsoft offers a new life of defense for Enterprise. It not only provides the inherent advantage over traditional antivirus solutions but when used offers a trust model where applications must earn trust to run. It allows Enterprises to counter the threat of executable file-based malware such as .exe, .dll, etc.
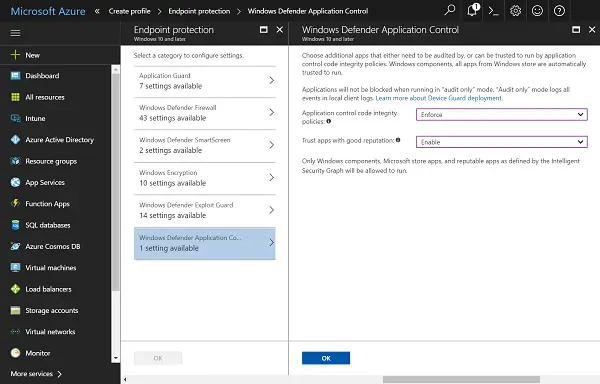
Windows Defender Application Control offers new capabilities
Starting with Windows 10 May 2019 update, Windows Defender Application Control works in conjunction with features like Windows Defender Application Guard. It provides hardware-based isolation of Microsoft Edge for enterprise-defined untrusted sites, to strengthen the security posture of Windows 10 systems.
Here is the list of Windows Defender Application Control(WDAC) features:
- File path rules, including optional runtime admin protection checks
- Multiple policy file support with composability
- Disabling script enforcement rule option
- Application Control CSP
- COM object registration support in policy
1] File path rules, including optional runtime admin protection checks
WDAC offers allow and dent riles based on the file path. When an application runs, the path is checked against the rules. It can only run when it matches the path. The administrator or higher privileged accounts can only set this path.
2] Multiple policy file support with composability
Since there are multiple business groups in a company, everyone might need their own set of policies. That’s where Supplemental polices came into the picture with this update. In simple words, a company can have an organizational policy and department policies.
3] Disabling script enforcement rule option
The feature will allow IT departments to tackle EXE, DLL, and driver enforcement without needing also simultaneously to address script host control.
We would suggest you read about Application Control CSP and COM object registration support in policy in complete details at Microsoft Security Page.
Leave a Reply