New findings from Kaspersky Labs signal some worrying facts. The report suggests Spam has emerged as the favorite tool for fraudsters to target Internet users. It also reports the mails with malicious attachments has increased significantly in the recent years.
The change in the target from web browsers to mails can primarily be attributed to enhanced security in browsers. Browser developers now implement security and anti-phishing protection tools. The additional layer of security makes it harder for cybercriminals to propagate their malware through infected web pages.
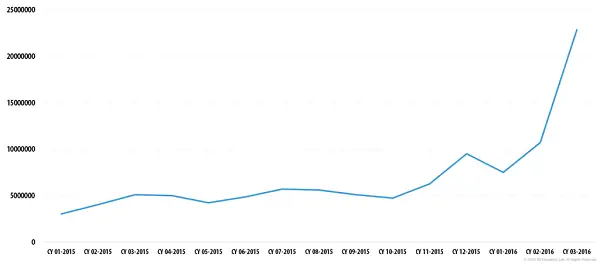
Th other facts in the report outline that the number of ransomware throughout the quarter has also increased. The main actor in this domain in Q1 was the ransomware Trojan Locky.
Locky ransomware is a malware that spreads via mass mailings with malicious loaders attached to spam messages. The malicious spam messages are bundled in attached DOC file with a macro that downloads the Locky Trojan from a remote server and executes it.
If the attack proves successful, Locky encrypts files with specific extensions (Office documents, multimedia content, etc.) on the user’s computer, and displays a message. The text of the message bears a link that directs a user to a site on the Tor network containing the cybercriminals’ demands. The ransomware has already been actively distributed via emails in different languages and has targeted at least 114 countries in all.
In Q1 2016 Kaspersky Lab registered 56.3% of spam in email flow which is 2.9 percent lower compared to the same period in 2015. The USA maintained its position as the biggest source of spam. Others, following the list are Vietnam and India. Russia has moved to seventh place this quarter with 4.9%.
If the report of the Kaspersky is to be believed, the quantity of spam emails has increased considerably. Moreover, there has been change in the method. Earlier, there were long emails with a detailed story. Now, it has been cut short.
Leave a Reply